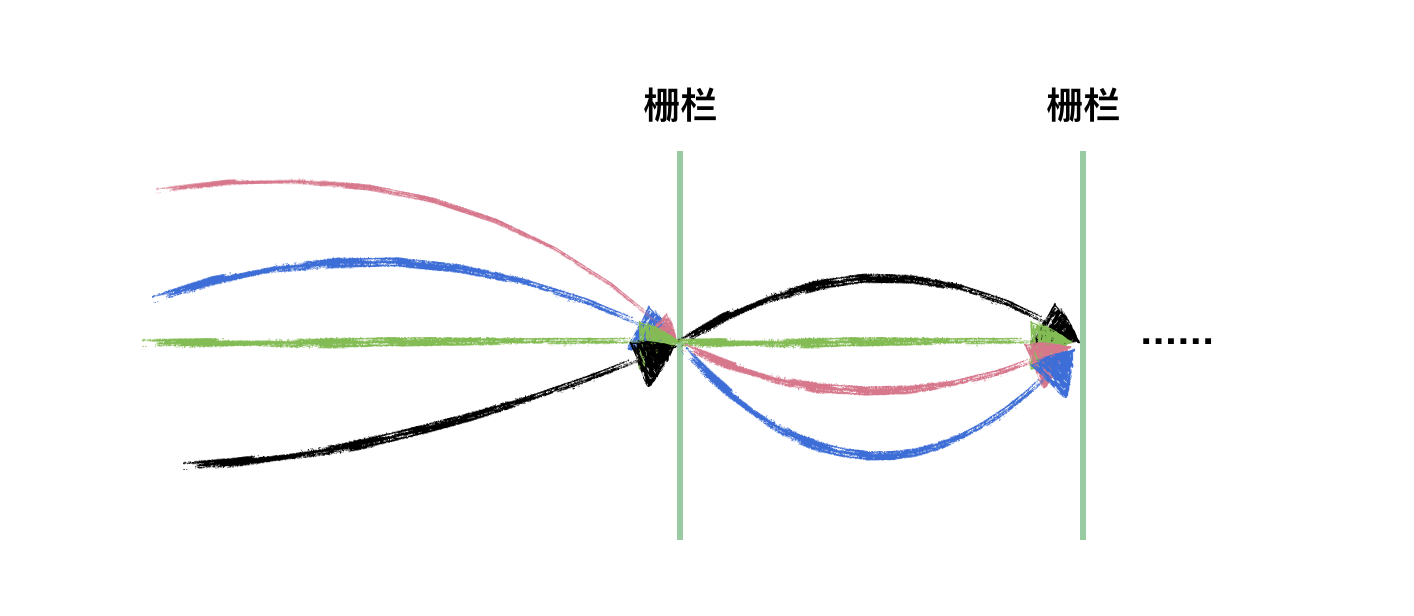
CyclicBarrier
使用
@Test
public void test() {
int threadNum = 5;
CyclicBarrier barrier =
new CyclicBarrier(
threadNum, () -> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 完成最后任务"));
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(
() -> {
try {
System.out.println(finalI + " 到达栅栏 A");
barrier.await();
System.out.println(finalI + " 冲破栅栏 A");
System.out.println(finalI + " 到达栅栏 B");
barrier.await();
System.out.println(finalI + " 冲破栅栏 B");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
})
.start();
}
}
原理
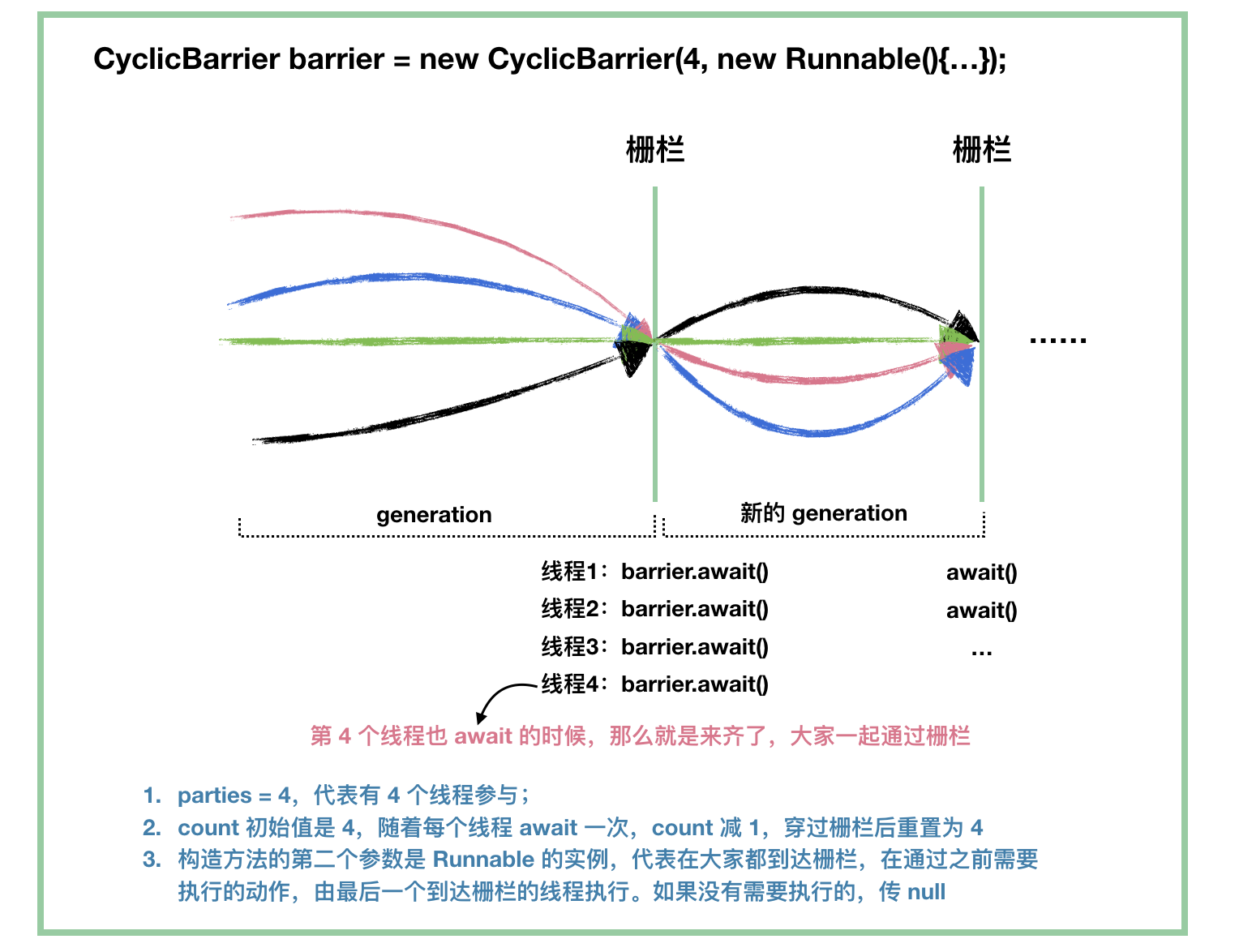
有两个构造方法,只有带Runnable参数的构造方法才会在所有线程都到达等待点之后执行Runnable里面的run方法。
CyclicBarrier(int parties) {
this(parties, null);
}
CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {
if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.parties = parties;
this.count = parties;
this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;
}
维护锁状态逻辑
其底层使用ReentrantLock+Condition进行锁状态的维护
// 维护锁状态
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition trip = lock.newCondition();
// 线程组数
private final int parties;
// 所有线程到达等待点后执行的Runnable
private final Runnable barrierCommand;
// 需要等待的线程数量
private int count;
// 屏障点定义
private static class Generation {
boolean broken = false;
}
具体看看其是如何实现等待逻辑的,线程等待需要调用await方法
public int await() {
return dowait(false, 0L);
}
public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit){
return dowait(true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
最终调用的是dowait方法
// 核心等待方法
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException, TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final Generation g = generation;
// 检查当前栅栏是否被打翻
if (g.broken) {
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
}
//检查当前线程是否被中断
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// 如果当前线程被中断会做以下三件事
// 1.打翻当前栅栏
// 2.唤醒拦截的所有线程
// 3.抛出中断异常
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 每次都将计数器的值减1
int index = --count;
// 计数器的值减为0则需唤醒所有线程并转换到下一代
if (index == 0) {
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
// 唤醒所有线程前先执行指定的任务
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null) {
command.run();
}
ranAction = true;
// 唤醒所有线程并转到下一代
nextGeneration();
return 0;
} finally {
// 确保在任务未成功执行时能将所有线程唤醒
if (!ranAction) {
breakBarrier();
}
}
}
// 如果计数器不为0则执行此循环
for (;;) {
try {
// 根据传入的参数来决定是定时等待还是非定时等待
if (!timed) {
trip.await();
}else if (nanos > 0L) {
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// 若当前线程在等待期间被中断则打翻栅栏唤醒其他线程
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// 若在捕获中断异常前已经完成在栅栏上的等待, 则直接调用中断操作
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
// 如果线程因为打翻栅栏操作而被唤醒则抛出异常
if (g.broken) {
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
}
// 如果线程因为换代操作而被唤醒则返回计数器的值
if (g != generation) {
return index;
}
// 如果线程因为时间到了而被唤醒则打翻栅栏并抛出异常
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
可以看到,是通过index字段控制线程等待的,当index不为0的时候,线程统一会进行阻塞,直到index为0的时候,才会唤醒所有线程,这时候所有线程才会继续往下执行。
重复使用
这个跟CountdownLatch不一样的是,CountdownLatch是一次性的,而CycliBarrier是可以重复使用的,只需调用一下reset方法。
public void reset() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 破坏当前的屏障点并唤醒所有线程
breakBarrier();
// 生成下一代
nextGeneration();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void breakBarrier() {
generation.broken = true;
// 将等待线程数量重置
count = parties;
// 唤醒所有线程
trip.signalAll();
}
private void nextGeneration() {
// 唤醒所有线程
trip.signalAll();
// 将等待线程数量重置
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}